Navigation: (click button to jump to module)
Introduction.
-
Welcome
-
Early Psychosis Basics
-
STEP Model of Care
-
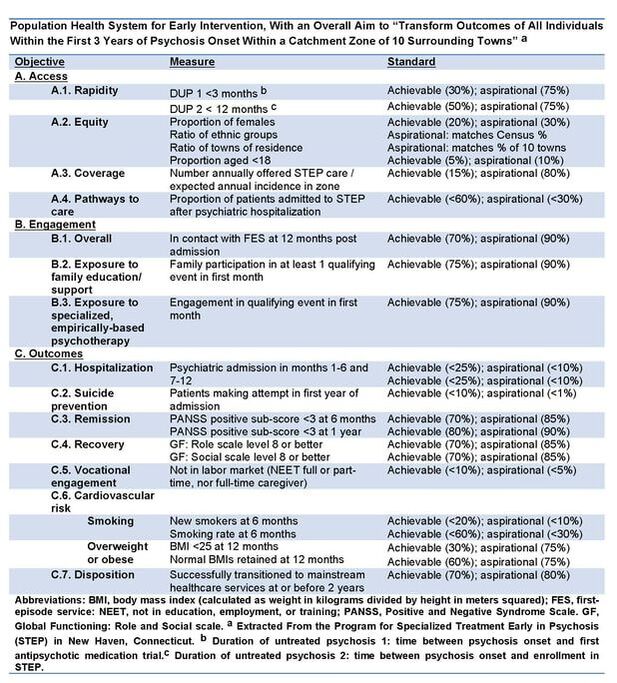
Population Health Approach
<
>
|
The STEP Learning Collaborative with the support of DMHAS and DCF aim to provide a resource library to support the development of mental health practitioners with the attitudes, knowledge and skills to effectively participate in a statewide system of care for individuals with recent onset psychotic disorders. This webpage features asynchronous content from various STEP Learning Collaborative offerings.
|
Early Psychosis Basics - Full Video (54:34)
Module A. Early Detection
-
Module A - Objectives
-
Early Detection
-
Duration of Untreated Psychosis (DUP)
<
>
Module A. Early Detection
- Knowledge: Importance of DUP, Pathways to Care and barriers, filters to delay, approaches to change stakeholder behavior, interaction with acute medical settings (ER, hospitals) and criminal justice settings (jail diversion)
- Skills: Screening for eligibility remotely (phone/Zoom), addressing ambivalence to enter treatment, addressing fears/concerns about mental healthcare, liaison with non-clinical settings (high schools, college counseling, clergy, community non-profits)
- Modality: mix of didactic webinar, directed reading and vignettes with role playing. Submit written plan for suggested improvement in access to local clinic.
What is the Duration of Untreated Psychosis (DUP)?
DUP is the time between onset of psychotic symptoms and effective treatment (e.g., antipsychotic treatment and/or admission to an early intervention for psychosis service)
Longer DUP is associated with:
•worse positive symptom severity
•worse negative symptom severity
•poorer rates of remission
•poorer social cognition
•cognitive impairment
Reducing DUP is associated with better outcomes (Birchwood, Todd, & Jackson, 1998):
•Clinical, functional, and cognitive benefits
•reducing the social consequences of psychosis onset
- social isolation
- unemployment
- homelessness
- deliberate self harm
- violence toward others
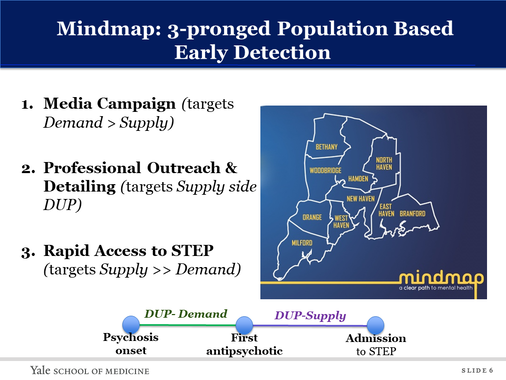
What is early detection?
Early intervention services for psychotic disorders optimally interlock strategies to deliver: (i) Early Detection (ED) (e.g., media campaigns, professional outreach and detailing, and rapid to shorten the time between onset of psychotic symptoms and effective treatment (DUP) and (ii) comprehensive intervention during the subsequent 2 to 5 years.
Early Detection strategies may include:
- Media Campaign (targets Demand > Supply)
- Professional Outreach & Detailing (targets Supply side DUP)
- Rapid Access to STEP (targets Supply >> Demand)
Recommended Readings:
Srihari VH, et al., Reducing the duration of untreated psychosis and its impact in the U.S.: the STEP-ED study. BMC Psychiatry. 2014 Dec 4;14:335. doi: 10.1186/s12888-014-0335-3. PMID: 25471062; PMCID: PMC4262386.
Module B. Case Formulation
-
Module B - Objectives
-
Case Formulation Template
-
Case Formulation Example
<
>
Module B: Case Formulation
- Knowledge: secondary psychosis (data elements including importance of collateral and revisiting history, labs, imaging etc.), initial med management to maximize safety, tolerability while eval is ongoing, assessing for and managing risk for aggression (towards self, others), family education, assessment of need, and engagement into care model, addressing basic needs and access to clinic, perspectives in pluralistic case formulation
- Skills: eliciting patient need, family/caregiver need, collecting data elements necessary for formulation, drafting 3 month templated case formulation with psychiatrist
- Modality: mix of didactic webinar, directed reading and writing of 3-month case formulation. Submit one complete case formulation from current personal caseload.
Coming soon...
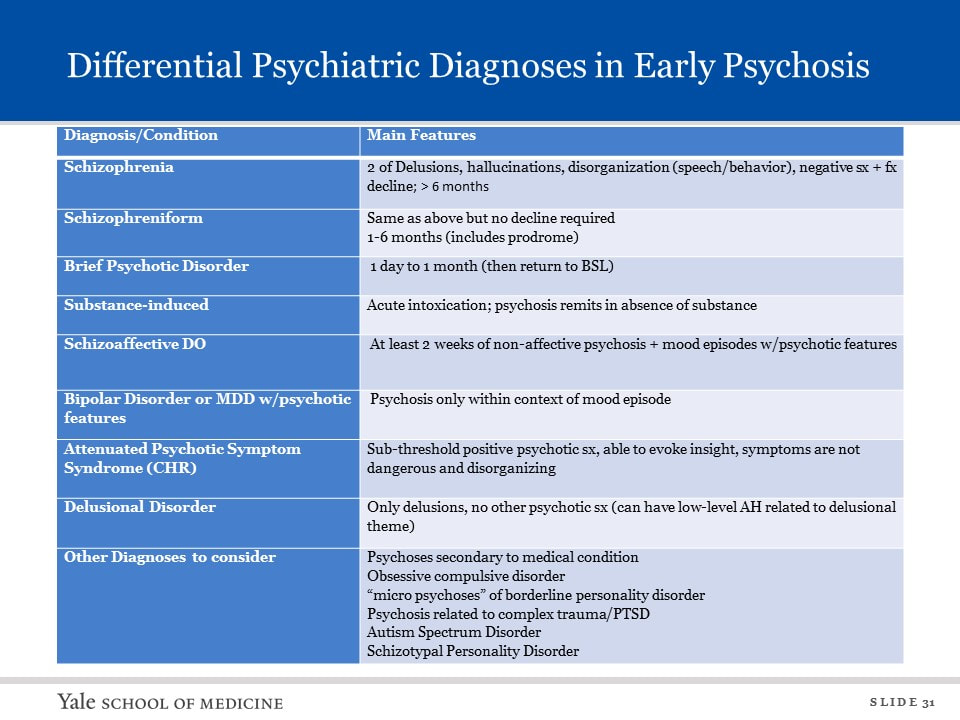
Developing Skills in Differential Diagnosis
-
Differential Psychiatric Diagnosis
-
Secondary Psychosis
-
Cultural Considerations
<
>
Secondary Psychosis Full Video (30:10)
Cultural Formulation Interview (CFI)
This evidence-based tool is composed of a series of questionnaires that assist clinicians in making person-centered cultural assessments to inform diagnosis and treatment planning.
Additional Resources for Culturally Responsive Care:
Young Adult American Born Muslims and Mental Health - ISPU
This evidence-based tool is composed of a series of questionnaires that assist clinicians in making person-centered cultural assessments to inform diagnosis and treatment planning.
Additional Resources for Culturally Responsive Care:
Young Adult American Born Muslims and Mental Health - ISPU
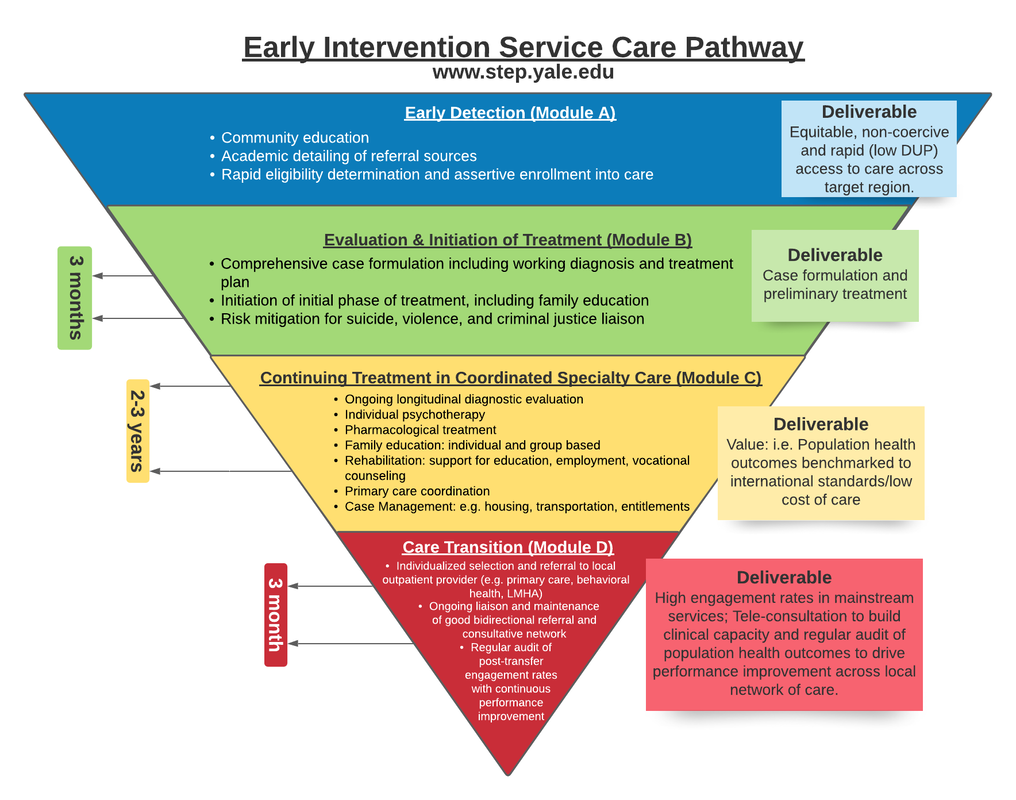
Module C. Coordinated Specialty Care (CSC)
-
Module C - Objectives
-
What is CSC?
-
Early Psychosis Treatment Approaches
<
>
Module C: Coordinated Specialty Care
- Knowledge: evidence for approach taken in main components of care (pharmacology, psychotherapy, family education, vocational support), social/structural determinants and responsive entitlement programs and relevant community supports, evidence for cardiovascular risk reduction efforts, women’s needs in early psychosis services, common sources of traumatic experience in FES samples, phases of illness
- Skills: using case formulation to integrate, prioritize components of care and align with phase of illness, working in an interdisciplinary team
- Modality: mix of didactic webinar, directed reading and vignettes. Submit reflection piece on how care approach with any current patient has changed in response to this training module.
"Coordinated specialty care (CSC) is a recovery-oriented treatment program for people with first episode psychosis (FEP). CSC promotes shared decision making and uses a team of specialists who work with the client to create a personal treatment plan. The specialists offer psychotherapy, medication management geared to individuals with FEP, family education and support, case management, and work or education support, depending on the individual’s needs and preferences. The client and the team work together to make treatment decisions, involving family members as much as possible. The goal is to link the individual with a CSC team as soon as possible after psychotic symptoms begin." - NIMH
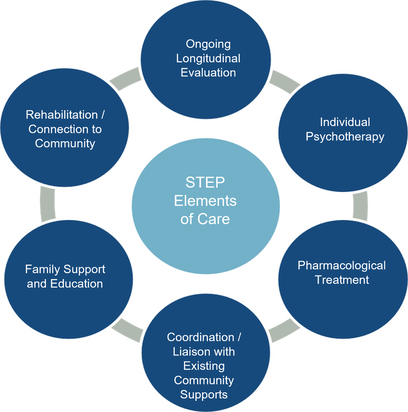
CSC Elements of Care
Overview of Early Psychosis Treatment Approaches - Full Video (48:29)
Psychoeducation.
-
Psychoeducation
-
Early Psychosis Overview
-
Stress Vulnerability
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Early Psychosis Overview - Full Video (20:18)
Stress Vulnerability Full Video (16:09)
Explore these links:
Psychosocial Approaches to Symptoms of Psychosis
-
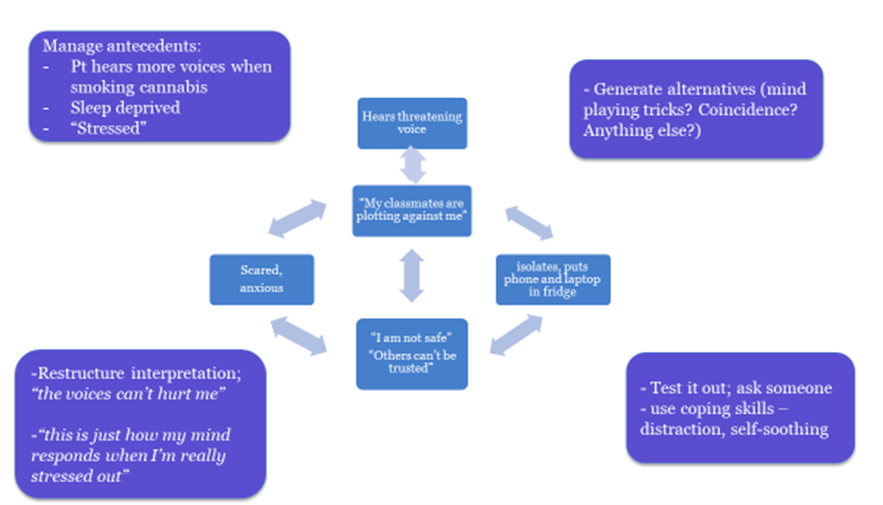
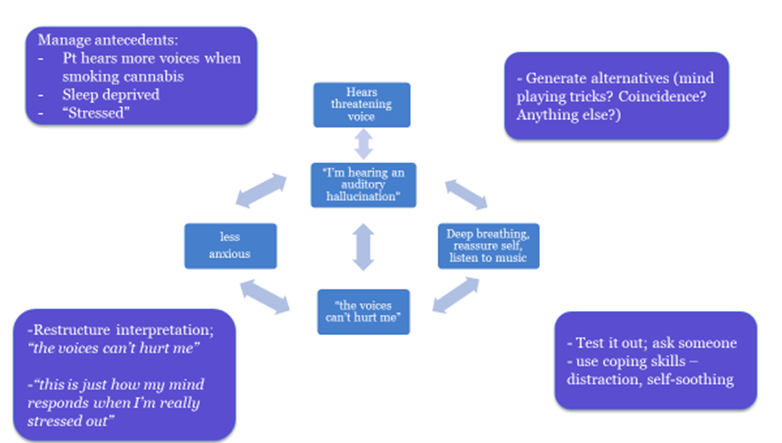
Positive Symptoms
-
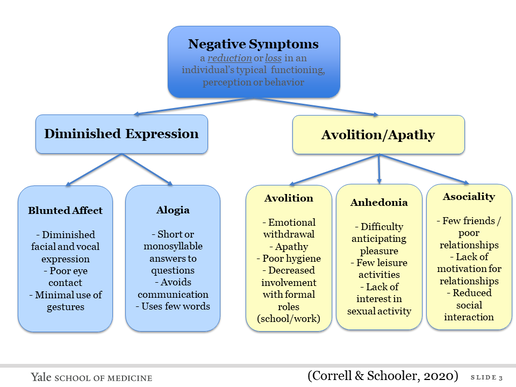
Negative Symptoms
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Empowering Families
-
Empowering Families
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Empowering Families - Full Video (28:08)
Family Orientation Workshop Example - Full Video (28:33)
Understanding and Addressing Substance Use
-
Cannabis and Psychosis
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Gone to Pot: The Complex Relationship between Cannabis, Cannabinoids, and Psychosis - Dr. Deepak Cyril D'Souza (44:35)
Cannabis and Psychosis Full Video (12:32)
Psychopharmacology.
-
FEP Prescribing Practices
-
Medication Guide for Primary Psychosis
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Antipsychotic Treatment for Early Course Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders (52:13)
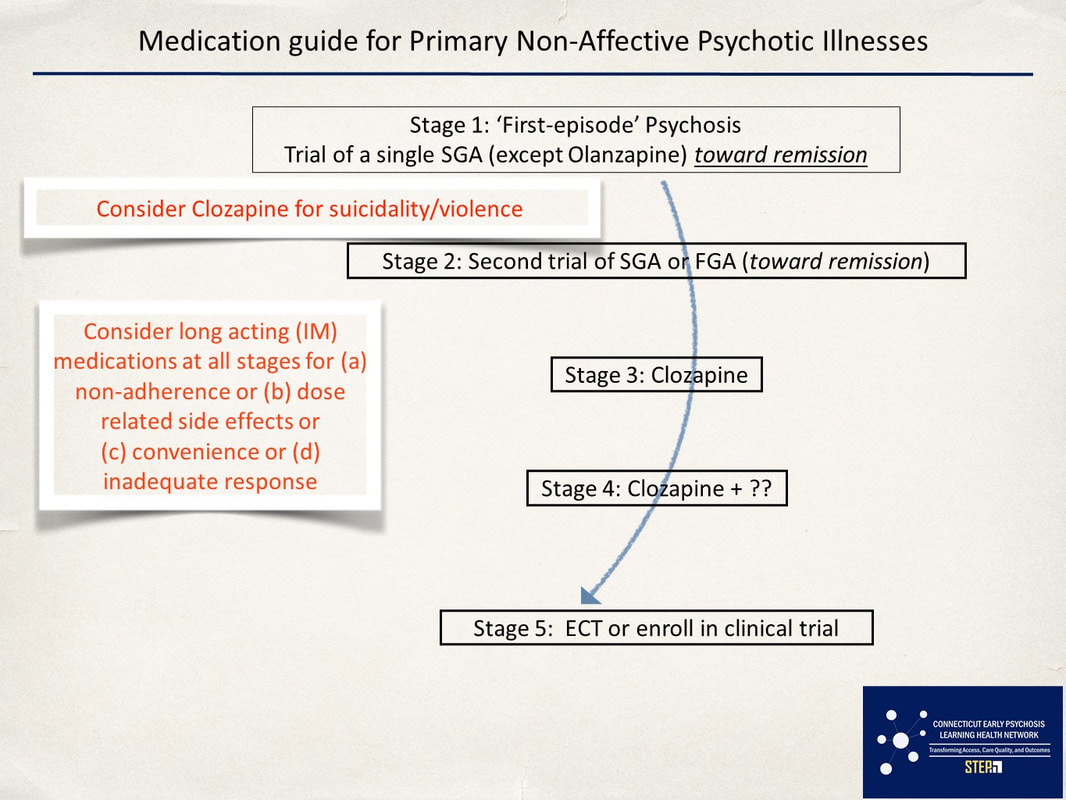
Medication Guide for Primary Non-Affective Psychotic Illnesses:
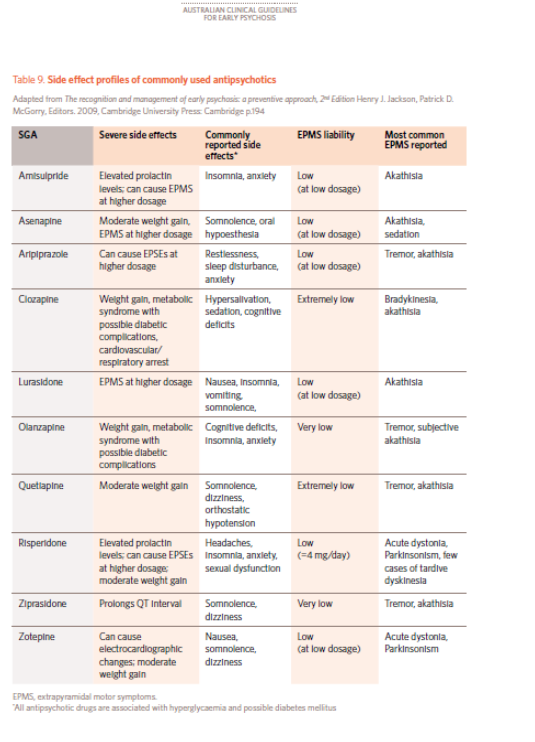
What to expect with antipsychotic medications:
Working with Risky Clients and Crisis Intervention.
-
Managing Risk in EIS
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Managing Crisis in an EIS - Full Video (35:33)
|
Handouts:
|
Recommended Readings:
Cole-King, A., Green, G., Gask, L., Hines, K., & Platt, S. (2013). Suicide mitigation: A compassionate approach to suicide prevention. Advances in Psychiatric Treatment, 19(4), 276-283. doi:10.1192/apt.bp.110.008763 Suicide. Chapter 6 in Havens LL: A Safe Place: Laying the Groundwork of Psychotherapy. Cambridge, Mass., Harvard University Press, 1989 |
The Role of Coordination |
-
Coordination
-
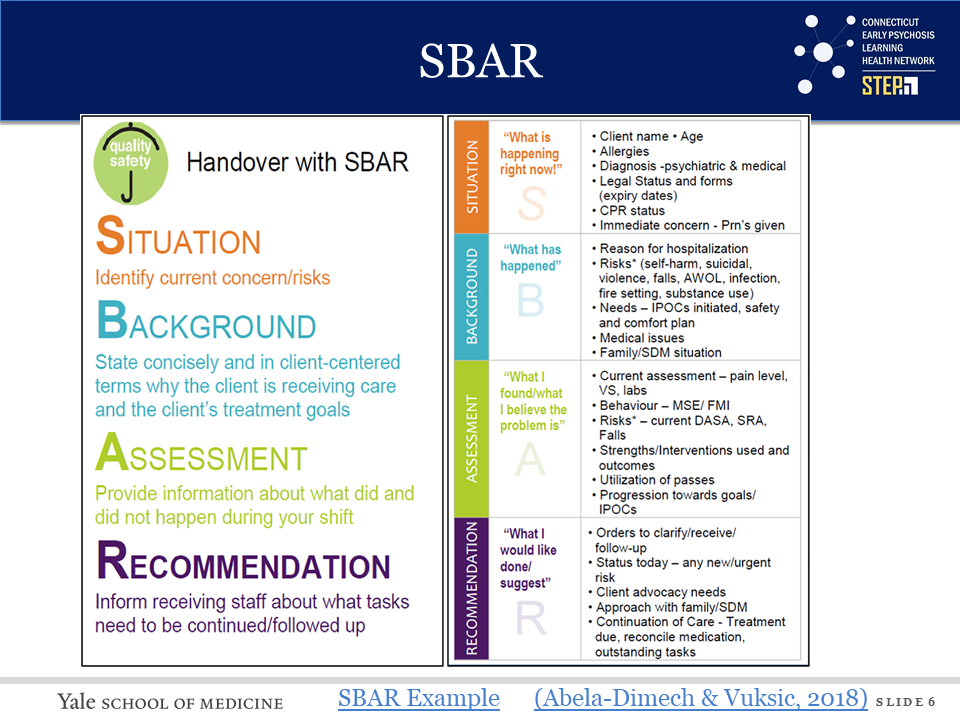
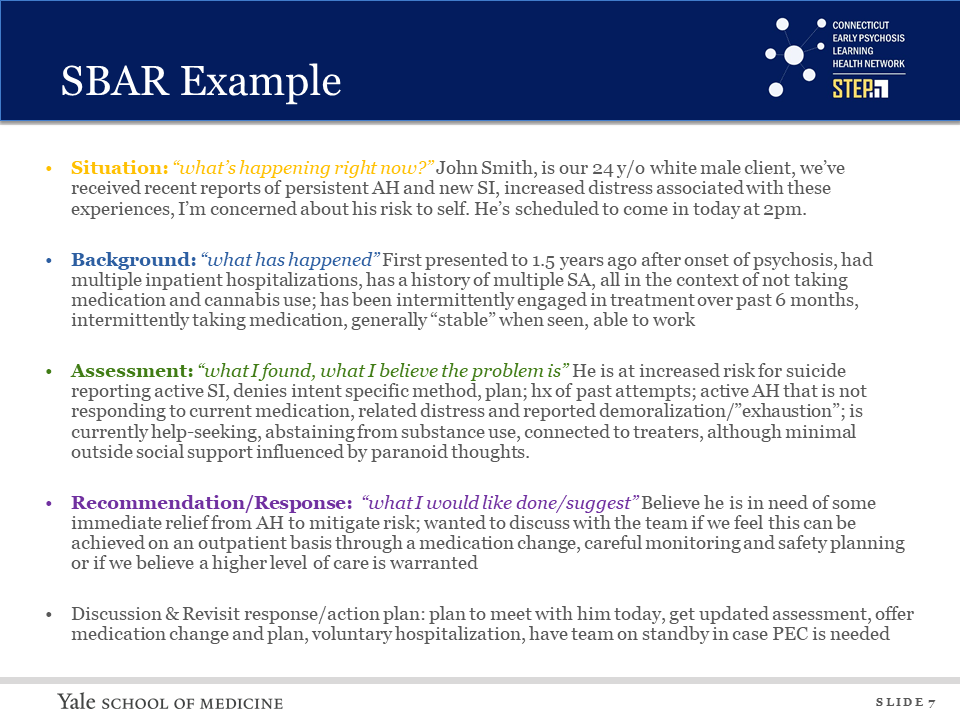
Communication
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Addressing Trauma
-
Trauma and Psychosis
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Connecting to Work, School, and Community
-
Supported Education and Employment
-
Peer Advocacy and Voices of Lived Experience
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
|
Cecilia McGough, talks with the STEP team about her lived experience of schizophrenia and the importance of advocacy for college students.
|
Fostering Health and Wellness.
-
Fostering Health and Wellness
-
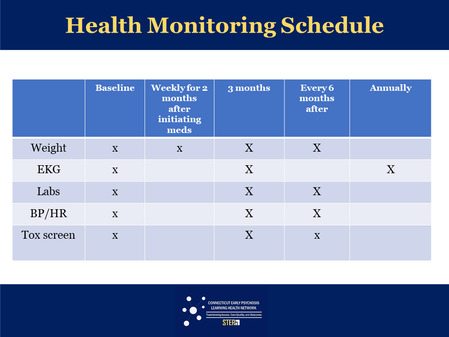
Schedule for Health Monitoring
<
>
Module D. Transitions of Care
-
Objectives
-
Transitions of Care
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Knowledge: evidence supporting need for careful handoff and f/u in FES, approaches taken by other teams, using phase of illness to calibrate and inform transition process
Skills: communication of condensed formulation with current needs to new provider, procedure to f/u in 1 and 3 months to audit and engage in performance improvement on handoff
Modality: mix of didactic webinar, directed reading and vignettes. Submit brief handoff note summarizing most current formulation with anticipatory guidance (updated and compressed version of formulation as in B), or reflection on barriers at your site to effective handoffs, or relapse prevention plan.
Skills: communication of condensed formulation with current needs to new provider, procedure to f/u in 1 and 3 months to audit and engage in performance improvement on handoff
Modality: mix of didactic webinar, directed reading and vignettes. Submit brief handoff note summarizing most current formulation with anticipatory guidance (updated and compressed version of formulation as in B), or reflection on barriers at your site to effective handoffs, or relapse prevention plan.
Supplemental Modules:
Clinical High Risk for Psychosis
-
Clinical High Risk for Psychosis
-
PRIME Clinic
-
Handouts and Links
<
>
Youth at CHR Full Video (37:58)
The PRIME (Prevention through Risk Identification Management and Education) Clinic identifies youth and young adults showing early signs of serious mental illness and provides treatment to prevent progression of illness.